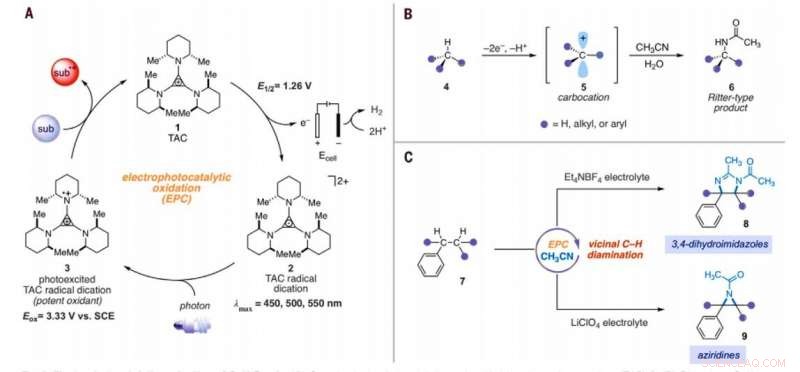
Elektrofotokatalytisk aminering av C – H -bindningar. (A) Generisk elektrofotokatalytisk cykel med trisaminocyklopropenium (TAC) 1. (B) Ritter-typ C-H-amineringsreaktion. (C) Elektrofotokatalytiska vicinala C – H -diamineringsreaktioner som rapporterats i detta arbete. Sub, substrat; subox, oxiderat substrat; Mig, metyl; Et, etyl; Ac, acetyl; Eox, oxidationspotential; lmax, våglängd för maximal absorption. Kredit:Vetenskap, 10.1126/science.abf2798
Oorganisk kemi, omvandlingen av inaktiverade kol-väte (C-H) bindningar till kol-kväve (C-N) bindningar är en högt värderad transformation. Forskare kan åstadkomma sådana reaktioner på endast ett C-H-ställe eftersom den första derivatiseringen kan minska reaktiviteten hos de omgivande CH-bindningarna. I en ny rapport som nu publicerats i Vetenskap , Tao Shen och Tristan H. Lambert vid institutionen för kemi och kemisk biologi, Cornell University, New York, visade att alkylerade arener kunde genomgå vicinala CH-diamineringsreaktioner för att bilda 1, 2-diaminderivat med användning av en elektrofotokatalytisk strategi. Under den syntetiska processen, de använde acetonitril som lösningsmedel och kvävekälla. De katalyserade reaktionen med hjälp av en trisaminocyklopropenium (TAC) -jon, som genomgick anodisk oxidation för att ge en stabil radikal dikation (vilken katjon som helst), medan den katodiska reaktionen reducerade protoner till molekylärt väte. När de bestrålade TAC-radikaldikationen med ett kompakt fluorescerande ljus i vitt ljus, de genererade en starkt oxiderande fotoexciterad mellanprodukt. Baserat på elektrolyten som används, laget erhöll antingen 3, 4-dihydroimidazol eller aziridinprodukter.
En ny syntetisk process
Allstädes närvarande kemiska reaktioner som omvandlar inerta kol-väte (C-H) bindningar till värdefulla kol-kväve (C-N) bindningar kan kraftigt påskynda konstruktionen av komplexa molekyler som är relevanta för det biomedicinska företaget. Forskare har därför härlett en serie C-H-amineringsreaktioner, men trots deras makt och omfattning, många syntetiska kampanjer måste installera många C-N-länkar. En stor utmaning för att utveckla kemiska sådana reaktioner är att heterofunktionalitet tenderar att inaktivera omgivande bindningar mot de typiska mekanistiska sätten för C -H -aktivering. Endast ett fåtal reaktionstekniker har hittills därför utfört multipotenta funktioner på proximala CH-bindningar. Shen et al. beskrev en strategi för potent oxidationskemi genom att kombinera ljusets och elektricitetens energi i en enda katalysator i en process som kallas elektrofotokatalys (EPC). Under denna strategi, laget använde elektrokemisk oxidation av trisaminocyklopropenium (TAC) -jon under en relativt mild elektrokemisk potential och samtidig bestrålning av synligt ljus för att excitera den resulterande radikala katjoniska mellanprodukten. Den foto-upphetsade radikala diceringen var en extremt potent oxidant som visade utmanande reaktioner inklusive oxidativa funktioner av bensen och andra elektronfattiga arenor eller regioselektiv C-H-funktionalisering av etrar.
Substrat omfattning av elektrofotokatalytisk vicinal C – H -diaminering. Alla utbyten är av isolerade produkter. Produkter erhölls som racemiska blandningar; kil- och streckavbildningar indikerar relativa stereokemiska relationer. (A) Diaminering av sekundära alkylbensener. (B) Diamination av primära alkylbensener. Experimentella detaljer tillhandahålls i kompletterande material. En asterisk anger körning vid 2,2 V; en dolk symbol (†) indikerar upparbetning med NaHCO3 (aq) och CH3OH; och en dubbel dolk dymbol (‡) indikerar nBu4NPF6 istället för Et4NBF4. SM, utgångsmaterial. Förening 36 avkylades vid upparbetning. Kredit:Vetenskap, 10.1126/science.abf2798 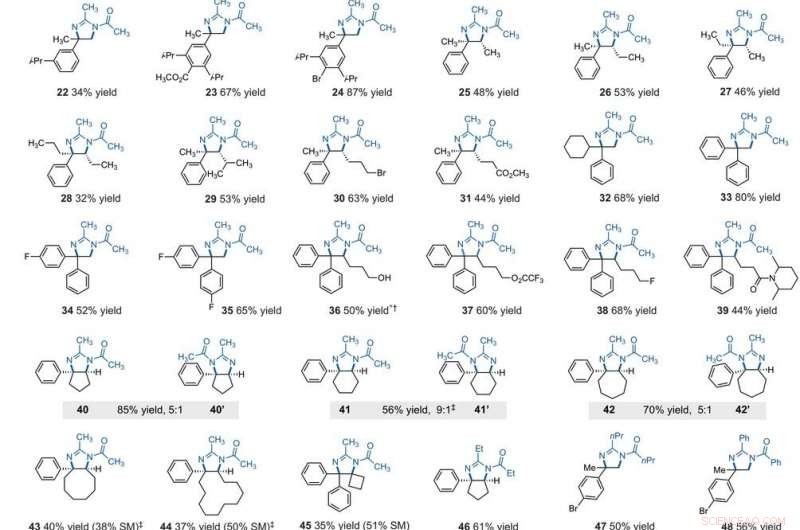
Teamet hypoteser TAC:s oxiderande kraft för att även möjliggöra andra CH-bindningsaktiveringsgrenrör. Under rätt förutsättningar, det elektrofotokatalytiska tillvägagångssättet skulle kunna generera karbo-katjon-mellanprodukter för att underlätta Ritter-funktionalisering av CH-bindningar utan en extern kemisk oxidant. Vanligtvis, under Ritter-typ reaktioner genererar en karbokation med efterföljande infångning av en nitril för att bilda nitriliumjonmellanprodukter följt av amidprodukter efter hydrolys. Teamet antog att de starkt oxiderande, ännu selektiva villkor som erbjuds av TAC (trisaminocyklopropenium) EPC (elektrofotokatalys) kan tillåta en sekvens av flera Ritter-typ H-funktionaliseringsreaktioner, där den initialt bildade acetamidgruppen underlättade en andra amineringsreaktion vid en angränsande position. Om det är möjligt, metoden kan underlätta regioselektiv amination av två C-H-bindningar helt enkelt med hjälp av synligt ljus, en mild elektrokemisk potential och ett vanligt lösningsmedel som kvävekälla istället för nitrenprekursorer. Shen et al. reported the realization of the electrophotocatalytic deamination of C-H bonds to furnish dihydroimidazoles or aziridines, depending on the type of electrolyte used during the experiments.
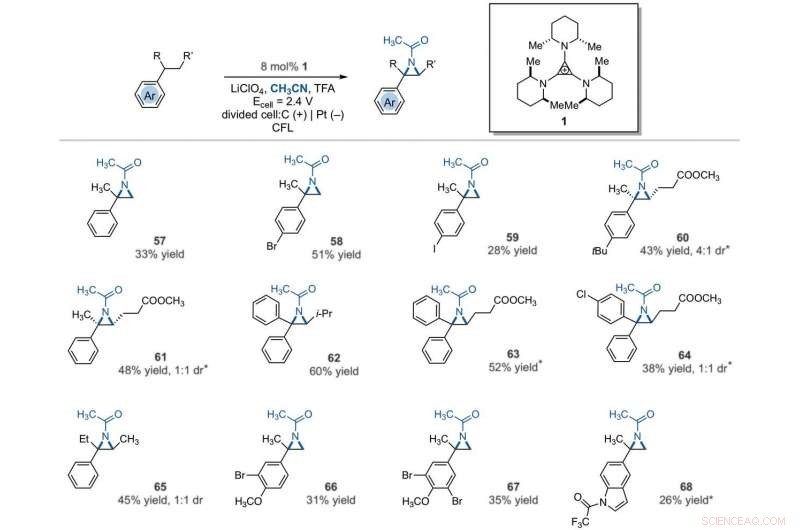
Electrophotocatalytic vicinal C–H aziridination. Detailed reaction conditions for each substrate are provided in the supplementary materials. Products were obtained as racemic mixtures; wedge and dash depictions indicate relative stereochemical relationships. An asterisk indicates run at 2.2 V. i-Pr, isopropyl. Kredit:Vetenskap, 10.1126/science.abf2798
The synthetic products
After extensively screening, the reaction conditions including the cell potential, electrolyte, acid additive and reaction time, Shen et al. identified conditions to assist the efficient conversion of a variety of benzylic hydrocarbons of the corresponding N-acyl-4, 5-dihydroimidazole adducts. In the reaction setup, the scientists used visible light irradiation with a white compact fluorescent light of a solution of the substrate containing TAC in a divided electrolytic cell under controlled potential. The team added the TAC catalyst and substrate within the anodic chamber where the C-H deamination chemistry occurred. The resulting redox by-product was effectively traceless. Based on similar conditions, a variety of benzylic hydrocarbons underwent vicinal C-H diamination to form diverse products. I samtliga fall, the researchers noted how the function of methylene carbons occurred in preference to methyl carbons, even when in the presence of a sterically demanding group or electron-withdrawing group. Since the α-α-diaryl amines formed a valuable substructure in biomedically relevant compounds, the team also investigated the transformation on gem-diaryl substrates. They found that the 1, 1-diphenyl ethane reacted efficiently to furnish a secondary alkyl benzene compound with 80 percent yield. The compatibility of alcohol, ester, alkyl fluoride and amide substituents allowed the synthesis of more highly functionalized adducts.
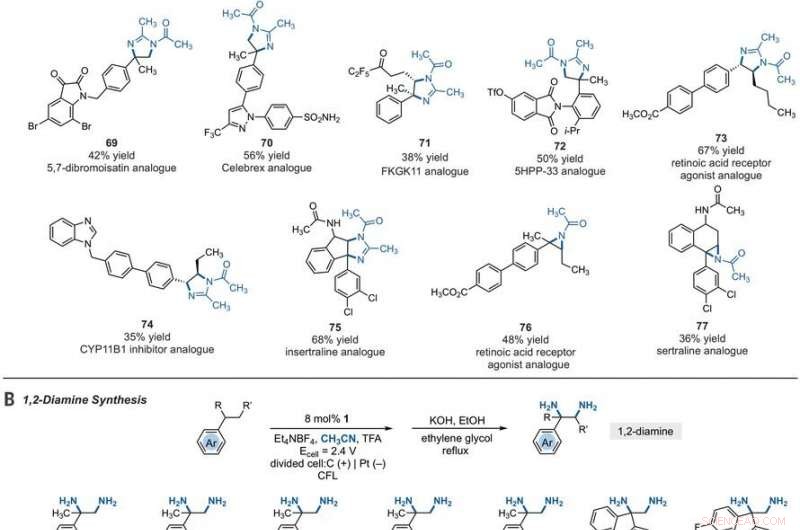
Synthetic applications of electrophotocatalytic vicinal C–H diamination. (A) Bioactive compound analogs prepared by means of electrophotocatalytic vicinal C–H diamination or aziridination. (B) 1, 2-Diamine synthesis. (C) Dihydroimidazole synthesis. (D) Bioactive compound synthesis. Detailed reaction conditions are provided in the supplementary materials. Products were obtained as racemic mixtures; wedge and dash depictions indicate relative stereochemical relationships. Products 80 and 81 were isolated as bis tosylate salts. Ph, phenyl; Tf, trifluoromethanesulfonate. Kredit:Vetenskap, 10.1126/science.abf2798
Functionalizing ring systems
The team further studied the potential of this reaction to functionalize ring systems. The reaction of phenyl cyclopentane led to the bicyclic compound in 85 percent yield. The scientists produced six- and seven-membered ring products as regioisomeric mixtures, alongside eight- and 12-membered ring products as single isomers. They improved some of the yields for cyclic substrates by using tetrabutylammonium phosphate (TBAF 6 ) as the electrolyte. In addition to acetonitrile, the researchers used other nitriles to give rise to diaminated products derived from propionitrile, butyl nitrile or benzonitrile as the nitrogen source. The scientists also tested the diamination process using unbranched benzylic substrates. Som ett resultat, imine and halogenated derivatives gave rise to aziridines in low to modest yields with nearly equal yields of diaminated products.
Mechanistic rationale for electrophotocatalytic vicinal C–H diamination. Voltages were measured in a 5:1 mixture of CH3CN and TFA to mimic the reaction conditions and are relative to SCE. Kredit:Vetenskap, 10.1126/science.abf2798 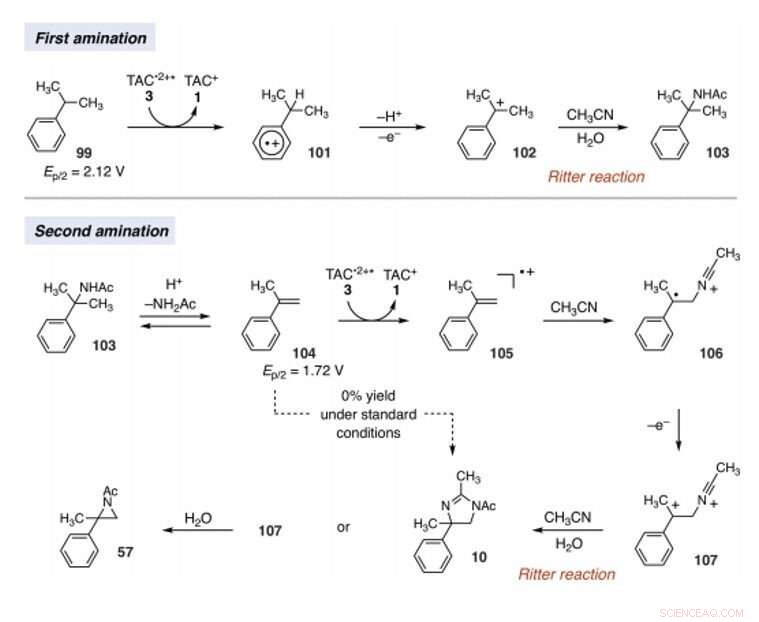
Since late-stage C-H functionalization processes offered powerful tools for the diversification of medicinal compound libraries, Shen et al. tested the difunctionalization chemistry on several molecules that are close analogs of known biologically active molecules. The team diaminated a dibromoisatin derivative to produce a bioactive molecule analogue in 42 percent yield. Till exempel, Isatin derivatives have been investigated in the past due to their medicinal properties including antitumor and antiviral activities. The scientists also found that celecoxib analogs could produce 56 percent yield under standard conditions. They then converted an analog of thalidomide with antiproliferative activity into another bioactive analog with 50 percent yield. The team further found how a small modification to the electrophotocatalytic procedure could lead to the isolation of free 1, 2-diamines in good yields. Shen et al. believe the mechanisms to have originated with Ritter-type amination of the substrates benzylic C-H bond in a process that accords with known electrochemical Ritter-type reactions. På det här sättet, Tao Shen and Tristan H. Lambert noted the compatibility of deamination with a reasonable diversity of functionality for the practical applications of this reaction. The scientists used the power of combined light and electrical energy to conduct the reactions in the functionality of a single catalyst with advancing synthetic capabilities.
© 2021 Science X Network